Research
Working Papers
Personal Bankruptcy, Entrepreneurial Financing, and the Economy [Paper]
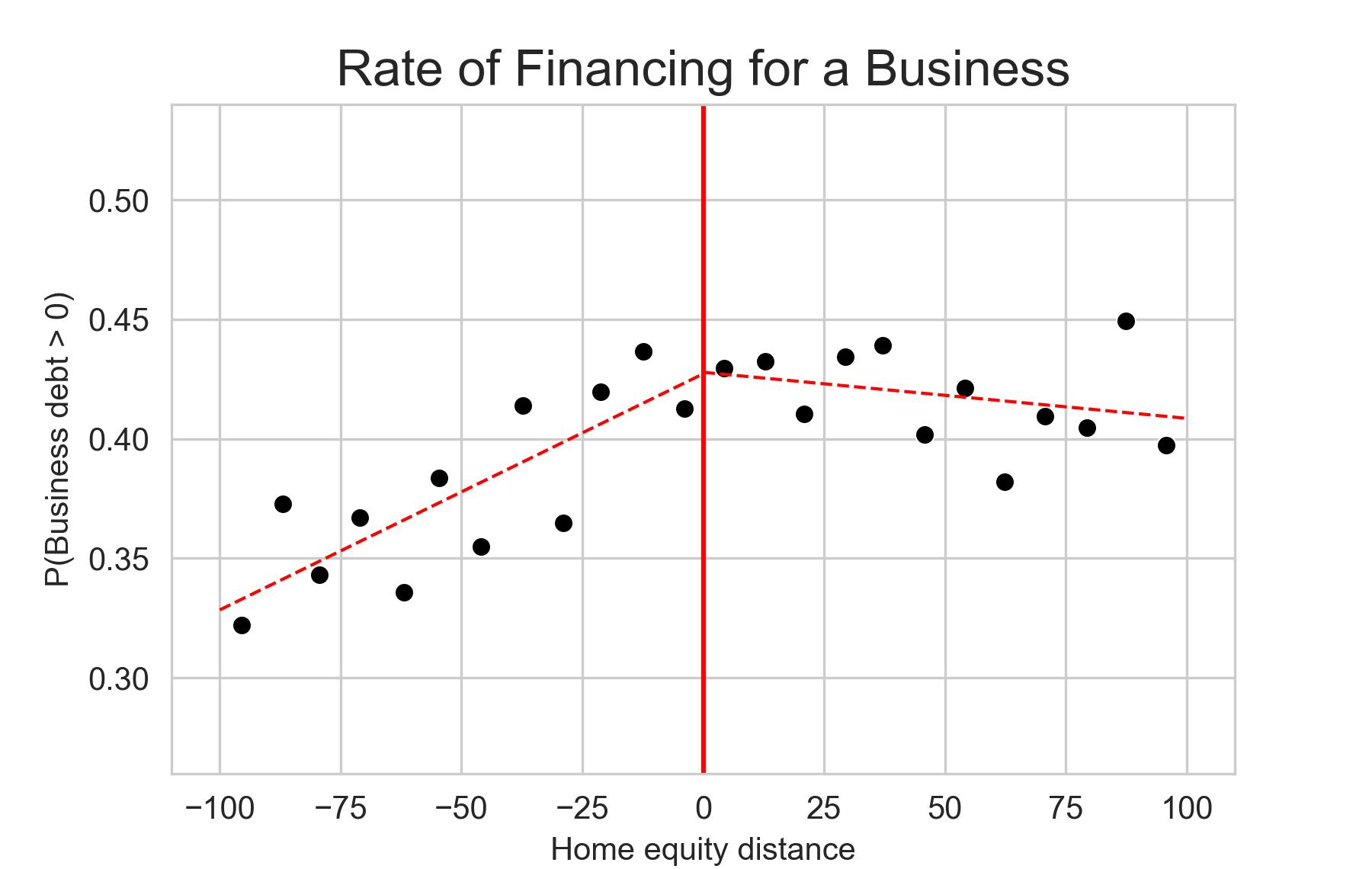
Abstract: Entrepreneurship inherently carries risk. The majority of businesses are unincorporated, meaning the business debts become personal liabilities for the owner. Consequently, when such a business falters, the owner may be incentivized to file for personal bankruptcy. This paper studies the impact of wealth protection on entrepreneurial activities. Utilizing a regression kink design, I establish a first causal link between potential debt forgiveness and entrepreneurial activities. My findings indicate that more lenient debt relief policies motivate business owners to finance their enterprises. Specifically, an additional $1,000 in potential debt forgiveness increases the probability of debt financing for their businesses by up to 0.2 percentage points (0.6 percent), and boosts business debt size by 0.3 percent. To investigate the mechanism behind this causal relationship, I introduce a quantitative general equilibrium model of household bankruptcy that integrates occupational choice. My results suggest that generous wealth protection can amplify U.S. entrepreneurial activities by reallocating capital towards more productive yet less wealthy entrepreneurs, enhancing productivity and economic output, and thus improving overall welfare. This effect is primarily driven by the insurance effect outweighing the interest effect: Even with higher borrowing costs, the financing rate and the size of debt increase in response to more generous debt relief.
Household Wealth and Business Dynamics
Abstract: This paper investigates the relationship between business size and household wealth. Using a large U.S. individual-level survey dataset from 1996 to 2013, I provide empirical evidence that the size of a startup is positively related to its owner’s wealth. Furthermore, this relationship holds among existing entrepreneurs; wealthier incumbent business owners experience faster business growth rates. This suggests that the inability to borrow may prevent entrepreneurs from starting their businesses at an optimal scale and afterward. However, as these analyses are descriptive, caution is required in interpreting them as causal relationships.